 |
GitHub Commander is a tool to access the GitHub API v3 from the CLI and automate otherwise tedious tasks. |
|---|---|
| Project |   |
| QA |  
|
| Release |  
|
Overview
GitHub Commander implements the gh command line tool,
which provides a ‘fluent’ interface
using click
(see Usage below).
It allows to access the
GitHub API v3
from a shell prompt for things usually done in the browser,
and also automates tasks that otherwise are tedious at best,
when done by clicking around on a web page.
GitHub Commander is powered by github3.py.
| Initially, the focus of the project will be to provide task automation, not completeness of covering every API aspect! |
|---|
Examples
To give you a quick impression of what this tool can do for you, here are some example calls:
$ gh user show foo
ACCOUNT Maciek Pacut [foo / User #33384]
SINCE/LAST 2008-11-08T18:01:02Z / 2015-03-30T21:35:31Z
URL https://api.github.com/users/foo
EMAIL maciek.pacut@gmail.com
REPOS/GISTS 14 ☑ ⎇ / -1 ☒ ⎇ / 0 ☑ ✍ / -1 ☒ ✍
STATS ⇦ ⋮ 1 / ⇨ ⋮ 0 / -1 ◔
$ gh label ls foo/ii
⎇ foo/ii
┌─────────────┬─────────┐
│ Name │ Color │
├─────────────┼─────────┤
│ maciekpacut │ #000000 │
└─────────────┴─────────┘
$ gh label export --format yaml jhermann/gh-commander to -
- {Color: '#fc2929', Name: bug}
- {Color: '#cccccc', Name: duplicate}
- {Color: '#84b6eb', Name: enhancement}
- {Color: '#159818', Name: help wanted}
- {Color: '#ededed', Name: in progress}
- {Color: '#e6e6e6', Name: invalid}
- {Color: '#cc317c', Name: question}
- {Color: '#ededed', Name: ready}
- {Color: '#ffffff', Name: wontfix}
$ gh label export waif rituals to labels.xls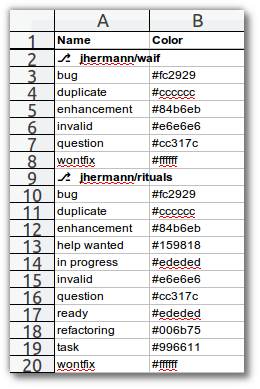
A Practical Use-Case
The following shows how to ease the management of a bunch of projects, via an Invoke task that synchronizes labels across a set of projects from a master definition.
import os
import tempfile
import requests
from invoke import ctask as task
PROJECTS = """
my/project
my/other-project
"""
PROJECTS = [i.strip() for i in PROJECTS.splitlines() if i]
LABEL_MASTER_URL = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jhermann/gh-commander/master/examples/labels.yaml'
@task(name='sync-labels')
def sync_labels(ctx):
"""Sync labels into managed projects."""
labels_yaml = requests.get(LABEL_MASTER_URL).text
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix='.yaml', prefix='gh-label-sync-', delete=False) as handle:
handle.write(labels_yaml)
try:
ctx.run('gh label import {} from {}'.format(' '.join(PROJECTS), handle.name))
finally:
os.remove(handle.name)See this tasks.py for the real-world application.
Installation
GitHub Commander can be installed via pip install gh-commander as usual,
see releases for an overview of available versions.
To get a bleeding-edge version from source, use these commands:
repo="jhermann/gh-commander"
pip install -r "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/$repo/master/requirements.txt"
pip install -UI -e "git+https://github.com/$repo.git#egg=${repo#*/}"See Contributing on how to create a full development environment.
To add bash completion, read the Click docs about it, or just follow these instructions:
cmdname=gh
mkdir -p ~/.bash_completion.d
_$(tr a-z A-Z <<<"$cmdname")_COMPLETE=source $cmdname >~/.bash_completion.d/$cmdname.sh
grep /.bash_completion.d/$cmdname.sh ~/.bash_completion >/dev/null \
|| echo >>~/.bash_completion ". ~/.bash_completion.d/$cmdname.sh"
. "/etc/bash_completion"Configuration
Login Credentials
Before you can use GitHub Commander, you have to provide some minimal configuration, most importantly credentials for API access. The recommended way for doing so is this:
- In the Settings › Applications of your GitHub account, press the “Generate new token” button of the “Personal access tokens” section, and follow the instructions. Copy the generated token to the clipboard, for use in the next step.
-
Create the file
~/.netrcwith the following contents (or add that to the existing file):machine api.github.com user «your GitHub username» password «your personal access token» Call
chmod 600 ~/.netrcto protect your sensitive data.
This way, the sensitive authentication information is separate from the rest of the configuration.
Use the gh help command to check whether your credentials actually work
– if they do, your GitHub user information is displayed, otherwise you'll get an error indicator.
Main Configuration File
TODO
Usage
Most of the commands are intentionally self-explanatory, so usually they are just listed without further details, in the hope that it's quite obvious what they do.
General Options
These options must appear before any sub-command, directly after gh.
-
--user ‹account name›– Override account name from config. -
--token ‹API token›– Override API token from config. -
--site ‹base URL›– Override site URL for on-premise installations of GitHub.
Common Options
Many of the commands do similar things, like exporting data.
That fact is reflected in some shared options that always behave the same.
See the --help message of every command for details and specific options.
-
--format ‹choice›– Specifies the output format to use, but is only needed in absence of a filename with a clear extension. The choices arejson,yaml,csv,xls, anddbf.
Common Arguments
-
‹repo›– A repository name, either fully qualified in the form‹account›/‹repo›, or else a plain repository name assumed to be owned by the current user.
Labels
-

gh label list ‹repo›… -

gh label export [--format=…] ‹repo›… [to] ‹filename.ext› -

gh label import ‹repo› [from] ‹filename.ext›
Users
-

gh user show [‹username›…]
Miscellaneous
-

gh help– Show information about the installation & configuration, and how to get further help.
Contributing
To create a working directory for this project, call these commands:
git clone "https://github.com/jhermann/gh-commander.git"
cd "gh-commander"
. .env --yes --develop
invoke ciSee CONTRIBUTING for more.
References
General
Similar Projects
Tools
Packages
Acknowledgements
- Logo elements from clker.com Free Clipart.