Glossary ¶
¶
External Glossaries
- Ice Cream Glossary by Dream Scoops (2017)
- Glossary of Ice Cream Types by Eater
- Hydrocolloid Glossary by Kitchen Alchemy
- Glossary for Manufacturing and Labeling
Alcohol by Volume (ABV)¶
Alcohol by volume can be taken literally, it specifies the percentage of pure ethanol contained in a beverage.
In the EU, "vol%" (volume percentage) is the usual way to express ABV.
In the US, "proof" is probably still quite common, it's essentially double the ABV value (80-proof ≅ 40 vol%).
Dextrose Equivalent (DE)¶
A measure of the amount of reducing sugars present in a sugar product (e.g. amount of monosaccharides in a glucose syrup), expressed as a percentage on a dry basis relative to dextrose. Note that syrups typically contain 25% water, while glucose powder (dehydrated / atomized glucose) only retains about 5%. In both cases, the DE value is the percentage of glucose molecules in dry matter.
DE and DP
The dextrose equivalent also gives an indication of the average degree of polymerisation (DP)
for starch sugars. As a rule of thumb, DE × DP = 120.
The difference of glucose syrup products to pure dextrose (100% glucose, a monosaccharide) is technically a reduced PAC (~90 instead of 190) and lower sweetness. Textural effects come from the remaining starches in glucose syrup, which contribute to the overall body, viscosity, and creaminess of the ice cream, and its melting behavior.
Freezing Point Depression Factor (FPDF)¶
See PAC.
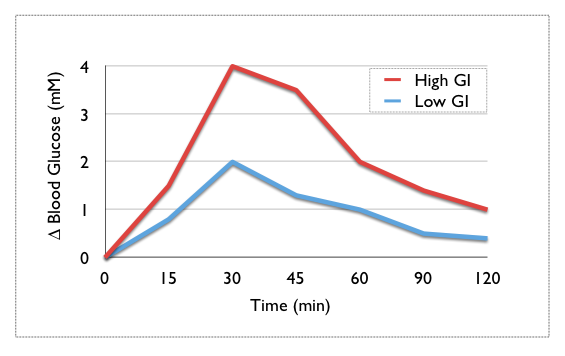
Glycemic Index (GI)¶
The GI is a measure of how quickly your blood sugar rises after consuming certain foods. Pure glucose is arbitrarily given the value of 100, and a GI of 55 or less is considered low, while 70 or more is classified as high, leaving the mid-range at 56 to 69.
Only foods that contain carbohydrates have a GI, while those with only fats and proteins do not, even though in people with diabetes, they can also affect the change rate of blood sugar.
Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB)¶
HLB is a numerical value assigned to emulsifiers to describe their balance between hydrophilic (water-loving) and lipophilic (oil-loving) properties.
It's a scale from 0 to 20, with 0 being highly lipophilic (oil-soluble) and 20 being highly hydrophilic (water-soluble).
HLB dictates the stability and performance of an emulsion. The HLB of the emulsifier needs to match the HLB requirements of the oil phase to create a stable emulsion.
Milk Solids Not-Fat (MSNF)¶
MSNF, also known as Solids Not-Fat (SNF), refers to all the solid components of milk excluding the fat and water. It's essentially a measure of the non-fat nutrients in milk, including proteins, lactose, vitamins, and minerals.
Generally, a good traditional ice cream contains 12% fat, 7-11% milk solids not-fat (11 for high fat), 15% sugar, 0.3% stabilizer and emulsifier, and 38.3% total solids.
For dairy, multiply the non-fat part by 0.093 to get the amount of MSNF in the milk serum (9.3%), if you have no better data like a dry mass percentage.
Potere Anti Congelante (PAC)¶
PAC is the same as FPDF but includes lactose, which constitutes 54.5% of MSNF. Typically SMP (skimmed milk powder) contains 97% MSNF, so 53% of lactose.
Different ingredients have different potentials to depress the FP, e.g. dextrose is almost twice as effective as sugar (PAC 190). What this means is that lower amounts of ingredients with a higher PAC, when used instead of sugar, make your ice cream softer straight out the freezer and easier to scoop.
The PAC method should be used when lactose concentration significantly varies or is high enough to make the ice cream too soft.
Total FPDF
The formula is sum(weight[g] * specific FPDF) / total weight * 100 with the sum taken over all sweeteners (in 100g ice cream mix).
With a PAC of 5.9 the salt percentage should be added too, even when it is commonly in the low single digit percentages.
Ice cream stored at -18°C with a total FPDF of 20..25 will be easily scoopable, while <15 will be quite hard. Ice cream is considered soft enough when about 65% of the water molecules are frozen at serving temperature (e.g. -11°C).
For milk ice cream, target range is 24-28 (double the serving temp, i.e. -12°C), for sorbets 30-36 (factor 2.5).
Potere Dolcificante (POD)¶
POD measures the sweetness of an ingredient relative to sucrose (table sugar). It is also known as PS (Pouvoir Sucrant) in France and SP (Sweetening Power) in the US.
By convention, the POD of sucrose is 100. Dextrose for example has a POD of 70, which means it is less sweet compared to the same amount of sugar. This can be used to change the PAC while keeping the POD stable, by using sucrose and dextrose (or other sweeteners with a higher PAC) in specific ratios.
Synergistic Interaction Gels (SIGs)¶
The interaction of specific thickeners can lead to the formation of gel networks, which influences the texture and mouth-feel of ice cream. These gels influence ice crystal formation by capturing water molecules, and also can simulate the presence of missing fat.
SIGs are typically more potent and sometimes have new characteristics compared to the isolated use of their components.
A typical example is the combination of LBG and XG.
Ultra Processed Food (UPF)¶
UPFs are industrially produced foods that have been significantly altered from their original state.
UPFs undergo extensive industrial processing, including chemical processes and additives, to alter their composition and properties. They often are ingredients not typically found in home cooking, such as preservatives, emulsifiers, sweeteners, artificial flavors, and colors.